Ipconfig For Mac
Displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings. Used without parameters, ipconfig displays Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) and IPv6 addresses, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adapters.
- Mac OS X ipconfig. The first thing ipconfig can do for you is quickly give you all your dhcp info: $ ipconfig getpacket en0 op = BOOTREPLY htype = 1 flags = 0 hlen = 6 hops = 0 xid = secs = 0 ciaddr = 0.0.0.0 yiaddr = 192.168.9.30 siaddr = 0.0.0.0 giaddr = 0.0.0.0 chaddr = 0:16:cb:8d:38:f7 sname = file = options: Options count is 7.
- Ipconfig is a utility that communicates with the IPConfiguration agent to retrieve and set IP configuration parameters. It should only be used in a test and debug context. Using it for any other purpose is strongly discouraged.
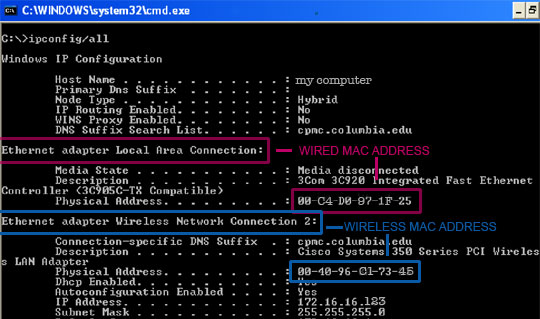
Nov 18, 2008 In the terminal window type:- ipconfig /all The text produced will include the MAC address of your laptop's Ethernet and Wireless cards. Jun 08, 2019 MAC ID is like a serial nr of your network card. On a windows system you can know what you’re mac id is through START RUN type “cmd” without the quotes type “ipconfig /all” without the quotes. In the list you’ll see the MAC ID is listed (sometimes it’s called Physical Address instead of MAC ID). Ipconfig Mac – Just like you you can open command prompt in Windows and hit “ipconfig” to get your local LAN/WLAN IP address, you have the same option on a Mac in OS X with the command “ifconfig”. Simply open up the terminal, eg. By pressing cmd+space and typing “terminal”. Then type “ ifconfig ” and hit enter.
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| /all | Displays the full TCP/IP configuration for all adapters. Adapters can represent physical interfaces, such as installed network adapters, or logical interfaces, such as dial-up connections. |
| /allcompartments | Displays the full TCP/IP configuration for all compartments. |
| /displaydns | Displays the contents of the DNS client resolver cache, which includes both entries preloaded from the local Hosts file and any recently obtained resource records for name queries resolved by the computer. The DNS Client service uses this information to resolve frequently queried names quickly, before querying its configured DNS servers. |
| /flushdns | Flushes and resets the contents of the DNS client resolver cache. During DNS troubleshooting, you can use this procedure to discard negative cache entries from the cache, as well as any other entries that have been added dynamically. |
| /registerdns | Initiates manual dynamic registration for the DNS names and IP addresses that are configured at a computer. You can use this parameter to troubleshoot a failed DNS name registration or resolve a dynamic update problem between a client and the DNS server without rebooting the client computer. The DNS settings in the advanced properties of the TCP/IP protocol determine which names are registered in DNS. |
| /release [<Adapter>] | Sends a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server to release the current DHCP configuration and discard the IP address configuration for either all adapters (if an adapter is not specified) or for a specific adapter if the Adapter parameter is included. This parameter disables TCP/IP for adapters configured to obtain an IP address automatically. To specify an adapter name, type the adapter name that appears when you use ipconfig without parameters. |
| /release6[<Adapter>] | Sends a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCPv6 server to release the current DHCP configuration and discard the IPv6 address configuration for either all adapters (if an adapter is not specified) or for a specific adapter if the Adapter parameter is included. This parameter disables TCP/IP for adapters configured to obtain an IP address automatically. To specify an adapter name, type the adapter name that appears when you use ipconfig without parameters. |
| /renew [<Adapter>] | Renews DHCP configuration for all adapters (if an adapter is not specified) or for a specific adapter if the Adapter parameter is included. This parameter is available only on computers with adapters that are configured to obtain an IP address automatically. To specify an adapter name, type the adapter name that appears when you use ipconfig without parameters. |
| /renew6 [<Adapter>] | Renews DHCPv6 configuration for all adapters (if an adapter is not specified) or for a specific adapter if the Adapter parameter is included. This parameter is available only on computers with adapters that are configured to obtain an IPv6 address automatically. To specify an adapter name, type the adapter name that appears when you use ipconfig without parameters. |
| /setclassid <Adapter>[ | Configures the DHCP class ID for a specified adapter. To set the DHCP class ID for all adapters, use the asterisk (*) wildcard character in place of Adapter. This parameter is available only on computers with adapters that are configured to obtain an IP address automatically. If a DHCP class ID is not specified, the current class ID is removed. |
| /showclassid <Adapter> | Displays the DHCP class ID for a specified adapter. To see the DHCP class ID for all adapters, use the asterisk (*) wildcard character in place of Adapter. This parameter is available only on computers with adapters that are configured to obtain an IP address automatically. |
| /? | Displays Help at the command prompt. |
Remarks
- This command is most useful on computers that are configured to obtain an IP address automatically. This enables users to determine which TCP/IP configuration values have been configured by DHCP, Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA), or an alternate configuration.
- If the name you supply for Adapter contains any spaces, use quotation marks around the adapter name (example: 'Adapter Name').
- For adapter names, ipconfig supports the use of the asterisk (*) wildcard character to specify either adapters with names that begin with a specified string or adapters with names that contain a specified string. For example, Local* matches all adapters that start with the string Local and *Con* matches all adapters that contain the string Con.
Examples
To display the basic TCP/IP configuration for all adapters, type:
To display the full TCP/IP configuration for all adapters, type:
Apple makes no representations regarding third-party website accuracy or reliability. Information about products not manufactured by Apple, or independent websites not controlled or tested by Apple, is provided without recommendation or endorsement. Apple assumes no responsibility with regard to the selection, performance, or use of third-party websites or products. For additional information. Risks are inherent in the use of the Internet. How to search for a word in powerpoint on mac.
To renew a DHCP-assigned IP address configuration for only the Local Area Connection adapter, type:
To flush the DNS resolver cache when troubleshooting DNS name resolution problems, type:
To display the DHCP class ID for all adapters with names that start with Local, type:
To set the DHCP class ID for the Local Area Connection adapter to TEST, type:
Additional references
View and control IP configuration state.
Free fps games for mac. Take charge army snipers and combat attack on the enemy airplane fighters.
ipconfig is a utility that communicates with the IPConfiguration agent to retrieve and set IP configuration parameters. It should only be used in a test and debug context. Using it for any other purpose is strongly discouraged. Public API's in the SystemConfiguration framework are currently the only supported way to access and control the state of IPConfiguration.
The IPConfiguration agent is responsible for configuring and managing the IP addresses on direct, connectionless interfaces such as IEEE 802.3 Ethernet and IEEE 1394 FireWire. The IPConfiguration agent is a program bundle that is loaded and executed by the configd(8) process.
The IPConfiguration agent implements the client side of the DHCP and BOOTP protocols described in RFC951, RFC1542, RFC2131, and RFC2132. It also assigns and maintains static IP addresses. It can also allocate and assign a link-local IP address if DHCP fails to acquire an IP address.
In all cases, the IPConfiguration agent performs IP address conflict detection before assigning an IP address to an interface.
Examples
Display your routers ip address:
$ ipconfig getoption en0 router
192.168.0.1
Renew DHCP Lease
$ sudo ipconfig set en0 DHCP
Display all DHCP configuration details:
“A Connection Manager connection does not connect after being disconnected” - Title of Microsoft KnowledgeBase article
Related macOS commands:
Ipconfig In Terminal For Mac
airport - Manage Apple AirPort
ifconfig - Configure network interface parameters
netstat(1) - Networking information
netintro(4)
sysctl(8)
Equivalent Windows command: ipconfig - Configure IP (internet protocol configuration)
Ipconfig Equivalent For Mac
Some rights reserved